| Код | photo_camera | Remains | shopping_cart | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 050700 |  | Photodiode 32V 940nm 400nm~1100nm 5nA SMD,3.9x4.4mm Photodiode | всего: 87 pcs маг ДП: 87 pcs |
| EVERLIGHT | SMD,3.9x4.4mm | |||
| 050716 | 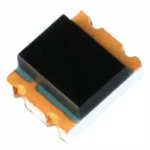 | Photodiode 32V 940nm 730nm~1100nm 10nA SMD-4P,2.7x3.2mm Photodiode | всего: 260 pcs маг ДП: 260 pcs |
| EVERLIGHT | SMD-4P,2.7x3.2mm | |||
| 050717 | 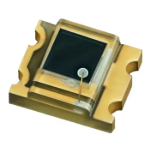 | Photodiode 32V 940nm 400nm~1100nm 10nA SMD-4P,2.8x3.3mm Photodiode | всего: 268 pcs маг ДП: 268 pcs |
| EVERLIGHT | SMD-4P,2.8x3.3mm | |||
| 050718 |  | Photodiode 32V 940nm 730nm~1100nm 5nA SMD,3.9x4.4mm Photodiode | всего: 84 pcs маг ДП: 84 pcs |
| EVERLIGHT | SMD,3.9x4.4mm | |||
| 050719 |  | Photodiode 32V 940nm 400nm~1100nm 5nA SMD,3.9x4.4mm Photodiode | всего: 84 pcs маг ДП: 84 pcs |
| EVERLIGHT | SMD,3.9x4.4mm |